Copyright 2012 neutronsources.org | All rights reserved. | Powered by FRM II | Imprint / Privacy Policy
Fourth Quarter Committee and Council Meetings Lead ESS into Second Year of Construction
Governance. SAC and TAC recommendations advance the European Spallation Source along the critical path to completion, and the ERIC Council gets rolling with the election of Prof. Caterina Petrillo as vice chair and approval of the instrument suite.
Date: 25/11/2015
Source: https://europeanspallationsource.se/

LUND— The European Spallation Source (ESS) ERIC Council elected Italian delegate Prof. Caterina Petrillo, head of the Physics and Earth Science Department at the University of Perugia, as Vice Chair at its late-October meeting. The Council also formally approved the entry into Phase 1 Engineering Design of the last four instruments recommended for construction in the instrument suite’s first 16 instruments.
The Council furthermore approved ESS management’s proposal, supported by the Scientific Advisory Committee’s to pursue the technical case of a spin-echo spectrometer and make a decision on if and how to realise it by the end of 2017.
The ESS Technical Advisory Committee submitted to the Council its report from the Committee’s extended mid-October meeting, TAC12, highlighting the many developments in the rapidly progressing technical areas of the project.
SAC14 Recommends Instrument Construction Sequence
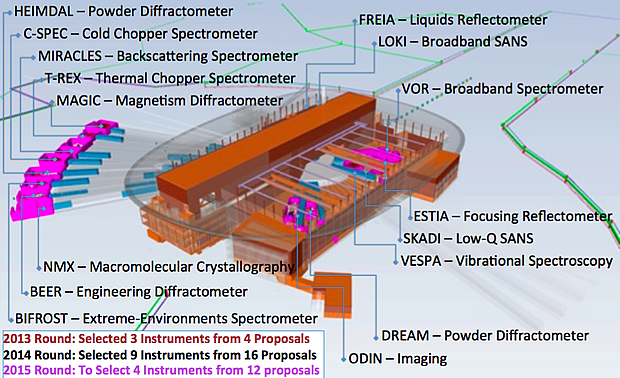
Over the last three years the European neutron science community has pulled together to identify the first 16 of the 22 instruments planned for ESS, a process in which the SAC has played a key part. The Committee’s September 28-29 meeting saw the full consolidation of this process with the caveat that a spin-echo instrument should also be provisioned in current planning.

“There is consensus that the chosen ESS suite of instruments is highly appropriate and achieves a balanced portfolio of science that encompasses both general purpose and higher risk instrumentation,” said ESS Director for Science Dimitri Argyriou, summarising the prevailing outlook of the meeting.
With the ERIC Council’s October approval of the instruments MAGIC, MIRACLES, T-REX and VESPA for Phase 1 development, the current challenge is to establish a construction schedule for the first 16 instruments. This is by necessity staggered, and the SAC and ESS management agree that a reasonable initial suite could contain the small-angle neutron scattering instruments LoKI and SKADI, the reflectometer ESTIA, the imaging instrument ODIN, diffractometers NMX, BEER and DREAM, and the spectrometers C-SPEC and T-REX.
The ESS Early Success Strategy calls for early commissioning of instruments that address large user communities and instruments that can provide high-impact science when the user program begins. Other important factors for instrument sequencing are the progress and technical maturity of the instrument projects thus far, the overall technical complexity of each instrument, and the availability of in-kind resources required to build the instrument.
New Emphasis on Science Support Systems
Noting that early scientific success requires more than commissioned instruments, the SAC entered into lengthy discussions on data handling solutions and Science Support Systems (SSS), particularly concerning the early work on instrument sample environment and support labs. The Committee recommended the formation of a Scientific and Technical Advisory Panel (STAP) for SSS.
A STAP is an independent advisory body composed of scientific experts from around the world, and ESS currently has STAPs for each instrument class. Aside from providing a mechanism for community input, the proposed SSS STAP would establish a close link between science support and instrument development. The Committee’s discussion also highlighted the progress made to develop a support lab for biological sample preparation in collaboration with the Lund University (LU) Protein Production Platform and the MAX IV Laboratory.
TAC12 Reaffirms Baselines and Details Progress on Test Facilities and Target Engineering
“TAC12 lasted for two full days and this is the new standard for future TAC meetings. The amount of work accomplished between meetings makes it necessary for them to be longer,” said ESS Technical Director Roland Garoby. “We are highly grateful to the Committee members for accepting to invest so much time in our project. The outcome of this meeting was well worth the efforts invested.”

With reports directly addressing recommendations and requests issued by TAC11, the Accelerator, Target and Integrated Control System (ICS) divisions brought the Committee up to date on the substantial progress since the Spring meeting. In the TAC’s estimation, these reports reaffirm the project’s schedule and budget baselines. The TAC furthermore welcomed the administrative reorganisation of the Accelerator and ICS divisions tailored to the goals of the ESS Construction Phase.
The pace of construction remains impressive, noted the TAC, with nearly three-quarters of the main Accelerator tunnel completed and series components entering into production. Key discussions and recommendations were made concerning the management of in-kind contributions relative to the tight schedule, communication across divisions, and the extensive recruitment and training still required for the Construction, Commissioning and Operations phases.
Building the Target, Accelerator and Integrated Control Systems
The TAC made many specific technical recommendations for the ESS target wheel, moderator, reflector and remote handling systems, demonstrating the advanced stage of engineering these Target division projects have achieved. In preparation for the next round of ESS licensing applications to the Swedish regulatory authorities, expected to take place in May 2016, several recommendations were also made regarding the Target Safety System and accident analysis.
TAC recommendations for the Accelerator project include prioritizing beam instrumentation requirements and assessing beam component installation resources. The Committee made special mention of the opportunities provided by the continuing development and use of test laboratory infrastructures in Lund and Uppsala, Sweden, not only for component testing but for technical training of personnel.

The present infrastructure of Uppsala University’s FREIA Laboratory is well prepared for imminent spoke cavity testing, remarked the Committee, and the test bench for a complete spoke cavity cryomodule is currently being constructed. Innovative engineering of the modulators at the modulator test facility at LU was cited as increasing efficiency and power capabilities for the ESS Accelerator while also reducing cost. Also highlighted by the TAC was the planning of an RF Integration test stand together with LU and CERN.
The ICS division gained new leadership this summer with the appointment of Henrik Carling as Head of Division, and seven new team members have been hired. The restructuring of the division, its Work Package configuration and in-kind activities was noted by the Committee as signalling good progress. The major recommendation was to pro-actively socialise the EPICS framework—an Open Source control system suite for scientific instruments that ESS will adapt to its needs—among in-kind partners and suppliers so that they will be adequately trained and prepared to contribute to the project.
Downloads
sac_tac_council_pdf.pdf
european_spallation_source_eric_council_meeting_3.jpg
essaerial_27october2015_acctarg.jpg